The break operator is used whenever we want to end a loop immediately, even before ending its execution in a natural way. Whenever the Break operator is met, the execution of the loop is immediately stopped and the program continues executing the first instruction that follows after the loop.
A loop termination using the Break operator can only be performed from within the loop’s body, and only on a iteration of the loop.
Let’s take the following example:
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
i++;
if (i > 10)
break;
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Loop has ended");
Console.Read();
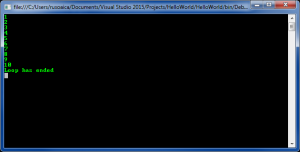
If you pay attention to that code, you will think that while (true) will make the loop run forever, because there will never be a condition to make it stop. However, inside that loop we are incrementing an integer, and use a conditional check that says “if our integer is greater than 10, use the break operator”; which, indeed, aborts the loop and continues the execution with the first instruction that follows after it, as you can see:
The concepts explained in this lesson are also shown visually as part of the following video:
Tags: break operator, operators, other operators